Tasks
ABC376
总结,acde题都能够在赛事大概读通题目,b题没看明白,
我感觉可能是自己的堆栈以及bfs还不够熟练
A
最近总是A就wa,好好反思一下哈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,c;
cin>>n>>c;
vector<int> a(n+1);
int res=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
int last=a[1];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]-last>=c){
res++;
last=a[i];
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
B
大致意思就是在环上移动到手的目的地的时候不能踩到另一只手
一开始这个代码不太行,应该是避开堵在中间的东西
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
int l=1,r=2;
int res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){
char h;
int t;
cin>>h>>t;
if(h=='L'){
if(t<=r){
res+=t-l;
l=t;
}else{
res+=(l+6-t);
l=t;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}else{
if(t>=l){
res+=t-r;
r=t;
}else{
res+=(r+6-t);
r=t;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
改进但wa了13个点
第一个判断少了abs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,q;
cin>>n>>q;
int l=1,r=2;
ll res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){
char h;
int t;
cin>>h>>t;
if(h=='L'){
if(t<=r&&l<r){
res+=abs(t-l);
l=t;
}else if(t<=r&&l>r){
res+=(t+n-l);
l=t;
}else if(t>r&&l<r){
res+=n-t+l;
l=t;
}else if(t>r&&l>r){
res+=abs(l-t);
l=t;
}
}else{
if(t<=l&&l>r){
res+=abs(t-r);
r=t;
}else if(t<=l&&l<r){
res+=(t+n-r);
r=t;
}else if(t>l&&l>r){
res+=n-t+r;
r=t;
}else if(t>l&&l<r){
res+=abs(r-t);
r=t;
}
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
jiangly gg的思路就是那么简单清晰

不动的那个在中间才需要绕路~
C
如果一开始就都能刚刚好装好就很好,答案就是那个没有盒子装的玩具的尺寸
如果都能装下,但是空隙浪费了?,那我们就从大到小的开始装
尽可能把大的先装完了去,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1),b(n);
map<int,int> mp;
int maxn=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
maxn=max(maxn,a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) cin>>b[i];
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
sort(b.begin(),b.end());
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
cout<<b[i]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int x=lower_bound(a.begin(),a.end(),b[i])-a.begin();
if(a[x-1]>b[i]||x==1&&a[x]>b[i]){
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
一开始胡乱倒腾
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int a[N],c[N];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> st(n+1),flag(n+1);
vector<pair<int,int>> b(n);
map<int,int> mp;
int maxn=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
maxn=max(maxn,a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
cin>>c[i];
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1);
sort(c+1,c+n);
int cnt=n-1;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
if(a[i]<=c[cnt]){
flag[i]=1;
st[cnt]=1;
cnt--;
}
}
int count=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(!st[i]){
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!flag[i]){
cout<<a[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
模仿佬二分,wa了一个点,估计是r取值不够
好吧,改成1e9也不行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1),b(n);
map<int,int> mp;
int maxn=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
cin>>b[i];
maxn=max(maxn,b[i]);
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
auto check=[&](int mid){
vector<int> c = b;
c.push_back(mid);
sort(c.begin(),c.end());
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]>c[i]) return false;
}
return true;
};
int l=0,r=maxn+1;
while(l<r){
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(check(mid)) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
if(!l||l==maxn+1) puts("-1");
else cout<<l<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
abc真是个小可爱,敢卡我1e9,🙂
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1),b(n);
map<int,int> mp;
int maxn=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) {
cin>>b[i];
maxn=max(maxn,b[i]);
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
auto check=[&](int mid){
vector<int> c = b;
c.push_back(mid);
sort(c.begin(),c.end());
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]>c[i]) return false;
}
return true;
};
int l=0,r=1e9+1,ans=-1;
while(l<r){
int mid=l+r>>1;
if(check(mid)){
r=mid;
}
else l=mid+1;
}
if(l==1e9+1) puts("-1");
else cout<<l<<endl;
return 0;
}
|
网友原本的贪心
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,a[200005],b[200005];
bool cmp(int x,int y){
return x>y;
}
signed main(){
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
scanf("%lld",&b[i]);
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
sort(b+1,b+n,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
if(b[i]>=a[i]){
continue;
}
else{
for(int j=i;j<=n-1;j++){
if(b[i]>=a[i+1]){
continue;
}
else{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",a[i]);
return 0;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",a[n]);
return 0;
}
|

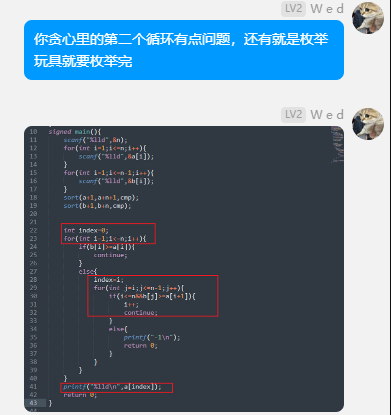
帮网友改的贪心
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,a[200005],b[200005];
bool cmp(int x,int y){
return x>y;
}
signed main(){
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
scanf("%lld",&b[i]);
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
sort(b+1,b+n,cmp);
int index=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(b[i]>=a[i]){
continue;
}
else{
index=i;
for(int j=i;j<=n-1;j++){
if(i<=n&&b[j]>=a[i+1]){
i++;
continue;
}
else{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
printf("%lld\n",a[index]);
return 0;
}
|
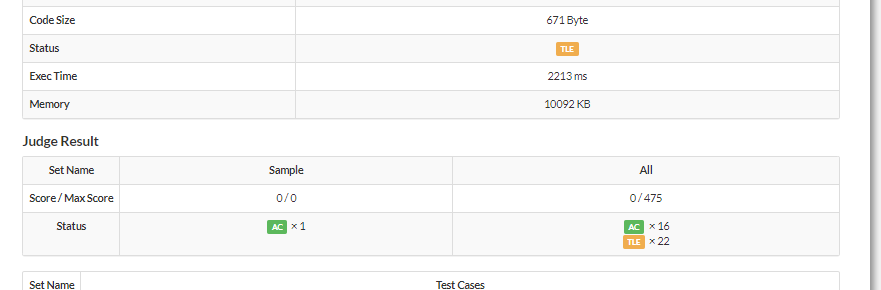
D
只能说难爆了,竟然轮到我用tarjan算法,虽然还是没有用tarjan做出来
如果回归最本质的问题,包含1的最小环是否能通过bfs求得,妈的,不就是用bfs求从1到1的最短路吗……
赛后第一打,wa了14个点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int d[N],st[N];
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
st[1]=1;
for(int i=h[1];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
d[j]=1;
st[j]=1;
q.push(j);
}
while(q.size()){
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=1;
if(t==1){
cout<<d[1]<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=h[t];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(!st[j]){
d[j]=d[t]+1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
puts("-1");
return ;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
|
借鉴了jiangly的,发现是和自己的思路差不多的,但是为什么自己写的就是错的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int d[N],st[N];
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
for(int i=h[1];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
d[j]=1;
q.push(j);
}
while(q.size()){
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(t==1){
cout<<d[1]<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=h[t];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(d[j]==0x3f3f3f3f){
d[j]=d[t]+1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
puts("-1");
return ;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int d[N],st[N];
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
for(int i=h[1];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
d[j]=1;
q.push(j);
}
while(q.size()){
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(st[t]) continue;
st[t]=1;
if(t==1){
cout<<d[1]<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=h[t];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(!st[j]){
d[j]=d[t]+1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
puts("-1");
return ;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
|
我好像悟了,因为会有自环啊老铁
st[j]=1和st[t]=1,在碰到自环的时候是有区别的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
int d[N],st[N];
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(d,0x3f,sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
d[1]=0;
st[1]=1;
for(int i=h[1];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(j==1){
cout<<2<<endl;
return;
}
if(!st[j]){
d[j]=d[1]+1;
st[j]=1;
q.push(j);
}
}
while(q.size()){
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=h[t];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(j==1){
cout<<d[t]+1<<endl;
return;
}
if(!st[j]){
d[j]=d[t]+1;
st[j]=1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
puts("-1");
return ;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
|
E
选的是下标,公式也是运用在下标。
动态规划行不行🙁
记忆化搜索不是得卡死
果不其然的卡飞了。

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
vector<ll> a(n+1),b(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>b[i];
vector<int> st(n+1);
ll res=1e18;
auto dfs=[&](auto&&dfs,int cnt,ll maxn,ll sum){
if(cnt>k) return;
if(cnt==k){
res=min(res,maxn*sum);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!st[i]){
st[i]=1;
dfs(dfs,cnt+1,max(a[i],maxn),sum+b[i]);
st[i]=0;
}
}
};
dfs(dfs,0,0,0);
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
下面这样去记录,maxn记录的是遍历过的最大值,没有恢复现场,如果maxn被改成6(案例二),那么在恢复0点再用1点的时候记录的最大时6,而不是拿max(a[2](上一层的maxn),a[3]),而是max(maxn,a[3])=6;

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
vector<ll> a(n),b(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>b[i];
vector<int> st(n+1);
vector<int> ans;
ll res=1e18;
auto dfs=[&](auto&&dfs,int cnt,ll maxn,ll sum){
if(cnt>k) return;
if(cnt==k){
if(res>maxn*sum){
res=maxn*sum;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(!st[i]){
st[i]=1;
ans.push_back(i);
dfs(dfs,cnt+1,max(a[i],maxn),sum+b[i]);
ans.pop_back();
st[i]=0;
}
}
};
dfs(dfs,0,0,0);
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
学习了jiangly gg的代码,发现搜索其实会浪费很多时间,因为是选择三个元素,最大值直接用排序找到就好了,而最小值,一定是小的和小的相加,成一个不算大的最大值。
枚举a[i]就好了,排除掉添加第i对元素的之前的最大值,这样是比较优秀的枚举方式
只有大的a[i]带着的b[i]小于前面的b[j]才有可能对最小值有贡献
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
vector<ll> a(n),b(n);
vector<int> ord(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>b[i];
iota(ord.begin(),ord.end(),0);
sort(ord.begin(),ord.end(),[&](int x,int y){
return a[x]<a[y];
});
priority_queue<int> q;
ll sum=0;
ll res=1e18;
for(auto i:ord){
sum+=b[i];
q.push(b[i]);
while(q.size()>k){
sum-=q.top();
q.pop();
}
if(q.size()==k) res=min(res,sum*a[i]);
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|